Autism Fact Sheet
What is Autism?
Autism (sometimes called classical autism) is the most common condition in a group of developmental disorders known as the autism spectrum disorders (ASDs).
Autism is characterized by impaired social interaction, problems with verbal and nonverbal communication, and unusual, repetitive, or severely limited activities and interests.
Other ASDs include Asperger syndrome, Rett syndrome, childhood disintegrative disorder, and pervasive developmental disorder not otherwise specified (usually referred to as PDD-NOS). Experts estimate that three to six children out of every 1,000 will have autism. Males are four times more likely to have autism than females
What are some common signs of autism?
There are three distinctive behaviors that characterize autism:
1. Difficulties with social interaction
As early as infancy, a baby with autism may be unresponsive to people or focus intently on one item to the exclusion of others for long periods of time. A child with autism may appear to develop normally and then withdraw and become indifferent to social engagement. Children with autism may fail to respond to their name and often avoid eye contact with other people. They have difficulty interpreting what others are thinking or feeling because they can t understand social cues, such as tone of voice or facial expressions, and don t watch other people s faces for clues about appropriate behavior. They lack empathy. Children with autism don t know how to play interactively with other children. Some speak in a sing-song voice about a narrow range of favourite topics, with little regard for the interests of the person to whom they are speaking.
2. Problems with verbal and nonverbal communication
They also tend to start speaking later than other children and may refer to themselves by name instead of I or me.
The hallmark feature of autism is impaired social interaction.
3. Repetitive behaviors or narrow, obsessive interests.
Many children with autism engage in repetitive movements such as rocking and twirling, or in self-abusive behavior such as biting or head-banging.
Many children with autism have a reduced sensitivity to pain, but are abnormally sensitive to sound, touch, or other sensory stimulation. These unusual reactions may contribute to behavioral symptoms such as a resistance to being cuddled or hugged. These behaviors can range in impact from mild to disabling. Parents are usually the first to notice symptoms of autism in their child.
Other associated conditions
Children with autism appear to have a higher than normal risk for certain co-existing conditions, including fragile X syndrome (which causes mental retardation), tuberous sclerosis(in which tumors grow on the brain), epileptic seizures, Tourette syndrome, learning disabilities, and attention deficit disorder.
For reasons that are still unclear, about 20 to 30 percent of children with autism develop epilepsy by the time they reach adulthood.
What causes autism?
Scientists aren t certain what causes autism, but it s likely that both genetics and environment play a role. Researchers have identified a number of genes associated with the disorder. Studies of people with autism have found irregularities in several regions of
the brain. Other studies suggest that people with autism have abnormal levels of serotonin or other neurotransmitters in the brain. These abnormalities suggest that autism could result from the disruption of normal brain development early in fetal development
caused by defects in genes that control brain growth and that regulate how neurons communicate with each other. While these findings are intriguing, they are preliminary and require further study. The theory that parental practices are responsible for autism has now been disproved.
What role does inheritance play?
Recent studies strongly suggest that some people have a genetic predisposition to autism. In families with one autistic child, the risk of having a second child with the disorder is approximately 5 percent, or one in 20. This is greater than the risk for the general
population. Researchers are looking for clues about which genes contribute to this increased susceptibility. In some cases, parents and other relatives of an autistic child show mild impairments in social and communicative skills or engage in repetitive behaviors. Evidence also suggests that some emotional disorders, such as manic depression, occur more frequently than average in the families of people autism
Do symptoms of autism change over time?
For many children, autism symptoms improve with treatment and with age. Some children with autism grow up to lead normal or near normal lives. During adolescence, some children with autism may become depressed or experience behavioural problems.
Tips for working with children with Autism
Make sure directions are given step by step verbally and visually and by providing physical supports or prompts, as needed by the child.
2. Individuals with autism often have trouble interpreting facial expressions, body language, and tone of voice. Be as concrete and explicit as possible in your instructions and feedback to the student.
3. Find out what the indivisuals strength are andemphasize them. Tap into those avenues and create opportunities for success.
4. Positive feedback and a lot of opportunities and practices.
5. Have consistent routines and schedules. If you know of the change in routine inform the child in advance to prepare him for the change.
What is autism?
Autism (sometimes called classical autism) is the most common condition in a group of developmental disorders known as the autism spectrum disorders (ASDs).
Autism is a general term for a group of complex disorders of brain development. Autism occurs when a child has trouble communicating and understanding what people think and feel. This makes it very difficult for autistic children to respond to gestures, facial expressions, touch and even language.
Experts estimate that three to six children out of every 1,000 will have autism. Males are four times more likely to have autism than females.
Types of Autism
- Autistic Disorder (also called “classic” autism)
This is what most people think of when hearing the word “autism.” People with autistic disorder usually have significant language delays, social and communication challenges, and unusual behaviours and interests. Many people with autistic disorder also have intellectual disability. - Asperger Syndrome
People with Asperger syndrome usually have some milder symptoms of autistic disorder. They might have social challenges and unusual behaviours and interests. However, they typically do not have problems with language or intellectual disability. - Pervasive Developmental Disorder – Not Otherwise Specified (PDD-NOS; also called “atypical autism”)
People who meet some of the criteria for autistic disorder or Asperger syndrome, but not all, may be diagnosed with PDD-NOS. People with PDD-NOS usually have fewer and milder symptoms than those with autistic disorder. The symptoms might cause only social and communication challenges.
Cause(s)of Autism.
Even with the amazing advancements in medical Science, Scientists are still unsure of the exact cause of autism.
- Scientists aren’t certain what causes autism, but it s likely that both genetics and environment play a role. Researchers have identified a number of genes associated with the disorder.
- Studies of people with autism have found irregularities in several regions of
the brain. Other studies suggest that people with autism have abnormal levels of serotonin or other neurotransmitters in the brain.
- These abnormalities suggest that autism could result from the disruption of normal brain development early in fetal development caused by defects in genes that control brain growth and that regulate how neurons communicate with each other.
- While these findings are intriguing, they are preliminary and require further study.
The theory that parental practices are responsible for autism has now been disproved.
Can Autism be Prevented?
- Since the exact cause of autism is not known, there is no definite solution to this question.
- However, it has been identified that exposure to certain chemicals during pregnancy can lead to an increase in the chance of autism to be prevalent in the child. Therefore, it is essential to avoid taking any drugs during pregnancy unless the doctor specifically prescribes them.
- It also is essential to avoid drinking alcoholic beverages of any kind during pregnancy. Being immunized against rubella (German measles) before becoming pregnant can prevent rubella-associated autism.
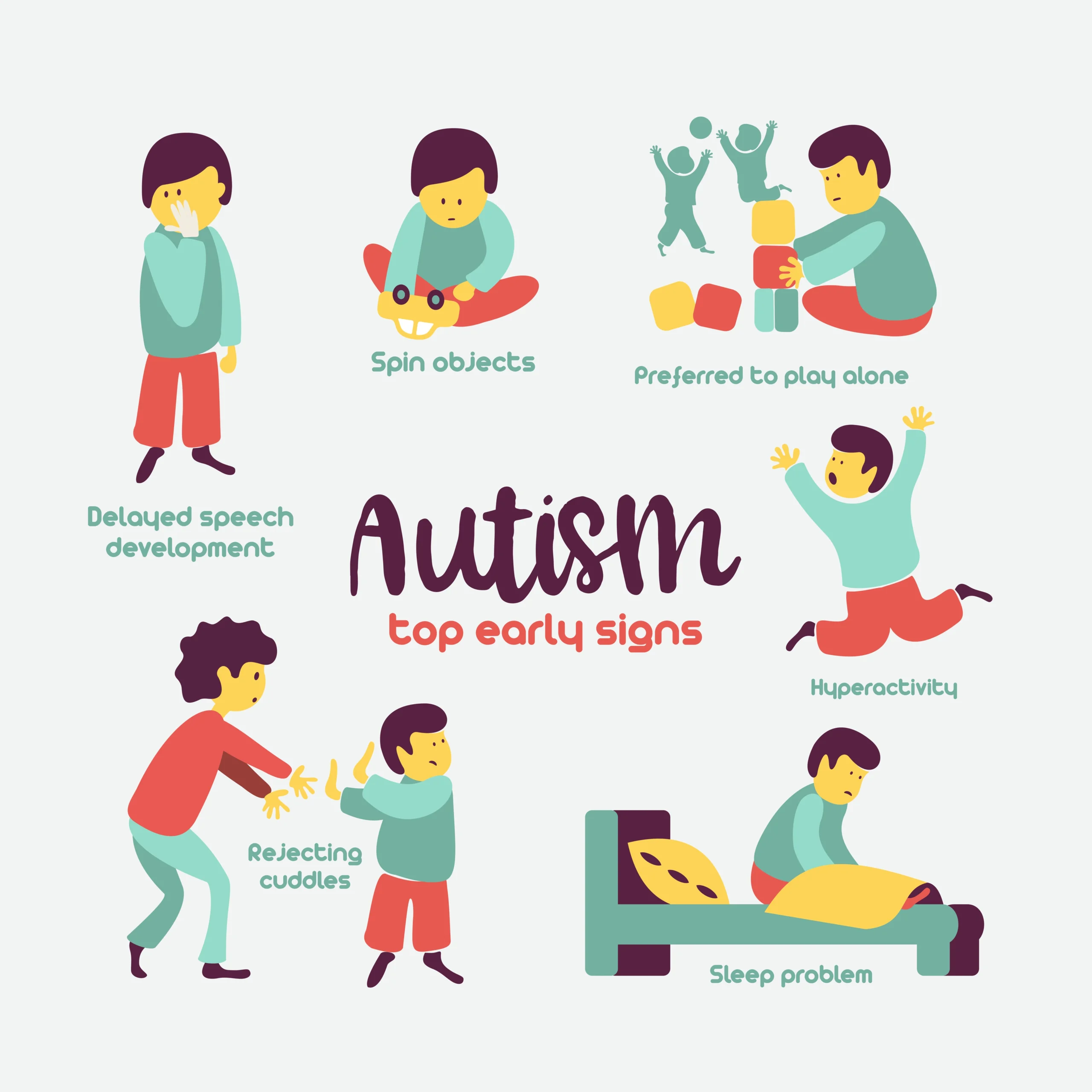
What are some common signs of autism?
There are three distinctive behaviours that characterise autism:
1. Difficulties with social interaction
- As early as infancy, a baby with autism may be unresponsive to people or focus intently on one item to the exclusion of others for long periods of time.
- A child with autism may appear to develop normally and then withdraw and become indifferent to social engagement. C
- Children with autism may fail to respond to their name and often avoid eye contact with other people.
- They have difficulty interpreting what others are thinking or feeling because they can t understand social cues, such as tone of voice or facial expressions, and don t watch other people s faces for clues about appropriate behaviour.
- They lack empathy.
- Children with autism don t know how to play interactively with other children.
- Some speak in a sing-song voice about a narrow range of favourite topics, with little regard for the interests of the person to whom they are speaking. It appears that they are in ‘their own world, in a bubble’
2. Problems with verbal and nonverbal communication
They also tend to start speaking later than other children and may refer to themselves by name instead of I or me. The hallmark feature of autism is impaired social interaction.
3. Repetitive behaviors or narrow, obsessive interests.
Many children with autism engage in repetitive movements such as rocking and twirling, or in self-abusive behaviour such as biting or head-banging.
Many children with autism have a reduced sensitivity to pain, but are abnormally sensitive to sound, touch, or other sensory stimulation. These unusual reactions may contribute to behavioural symptoms such as a resistance to being cuddled or hugged.
Common Misconceptions
- Children with autism can’t feel or express any emotion—happy or sad
- Their inability to express themselves verbally results in many people believing that they don’t want to make friends
- Children with autism are intellectually disabled ( In fact , quite a few kids have a higher IQ than the average child due to their enhanced ability to concentrate)
- Autism is caused by bad parenting.
Therapy
- There is no specific medicine to cure autism, but children can improve significantly with behavior and sensory therapies as part of autism intervention plan..
- Each child or adult with autism is unique and, so, each autism intervention plan should be tailored to address specific needs.
- Early intensive behavioral and sensory intervention involves a child’s entire family, working closely with a team of professionals. Many persons with autism have additional medical conditions such as sleep disturbance, seizures and gastrointestinal (GI) distress. Addressing these conditions can improve attention, learning and related behaviors.
Tips for working with children with Autism
- Make sure directions are given step by step verbally and visually and by providing physical supports or prompts, as needed by the child.
- Individuals with autism often have trouble interpretating facial expressions, body language, and tone of voice. Be as concrete and explicit as possible in your instructions and feedback to the student.
- Find out what the individuals strength are and emphasize them. Tap into those avenues and create opportunities for success.
- Positive feedback and lot of opportunities and practices.
- Have consistent routines and schedules. If you know of change in routine inform the child in advance to prepare him for the change.
Autism support group & websites
Autismsupport.in
Autismsocietyofindia.org
Autism.org.uk
ऑटिज्म क्या है?
विकास में बाधक होने वाली बीमारियों के समूह में ऑटिज्म एक है जिसे ऑटिज्म स्पेक्ट्रम डिसऑर्डर (एएसडी) के नाम से भी जाना जाता है।
जब बच्चे को बात करने में या लोग क्या सोच रहे हैं या महसूस कर रहे हैं, समझने में दिक्कत हो, तो यह ऑटिज्म हो सकता है। इससे अपने आप में खोये बच्चों को इशारे, चेहरे के भाव, छूने यहां तक कि भाषा का जवाब देना तक मुश्किल हो जाता है।
ऑटिज्म के कारण
वैज्ञानिकों को ऑटिज्म होने का निश्चित कारण नहीं पता, लेकिन इसमें आनुवाशिंक और वातावरण की भूमिका होती है। खोचकर्ताओं ने कुछ जीन्स की संख्या की पहचान की है जो इस विकार से संबंधित है। इन असामान्यताओं से पता लगता है कि जब भू्रण का शुरूआती विकास हो रहा होता है तो दिमाग के सामान्य विकास को नियंत्रित करने वाले जीन्स में दोष होने के कारण ही ऑटिज्म हो सकता है।
ऑटिज्म से पीडि़त लोगों पर हई रिसर्च में उनके दिमाग के कुछ हिस्सों में अनियमितताएं पाईं गई हैं।
एक अन्य रिसर्च में ऑटिज्म से पीडि़त मरीजों के दिमाग में सेरोटोनिन या अन्य न्यूरोट्रांसमीटर्स का असामान्य स्तर पाया गया है।
ऑटिज्म के लिए माता–पिता जिम्मेदार है, इस थ्योरी को अस्वीकार कर दिया गया है।
क्या ऑटिज्म को रोका जा सकता है?
– अभी तक ऑटिज्म का सटीक कारण नहीं ज्ञात हो पाया है, ऐसे में इस सवाल का भी निश्चित जवाब नहीं है।
– हालांकि, यह पता चला है कि गर्भावस्था के दौरान कुछ प्रकार के रसायनों से संपर्क में रहने से बच्चे में ऑटिज्म होने की संभावना बढ़ जाती है। इसीलिए डॉक्टर की सलाह के बिना गर्भावस्था के दौरान दवाइयां न लेना भी आवश्यक है।
– गर्भावस्था के दौरान एल्कोहिक पदार्थों के सेवन का परहेज भी आवश्यक है।
ऑटिज्म के सामान्य संकेत क्या हैं?
तीन प्रकार के विशेष व्यवहार हैं जिनसे ऑटिज्म को पहचाना जा सकता है।
1. सामाजिक व्यवहार में मुश्किलें होना
– बचपन में, ऑटिज्म से पीडि़त बच्चा लोगों को किसी तरह की प्रतिक्रिया नहीं देगा और आस–पास की चीजों को छोड़ किसी एक वस्तु पर लंबे समय के लिए ध्यान केंद्रित कर लेगा।
– ऑटिज्म वाले बच्चों का सामान्य विकास होता है और फिर वापस चले जाते हैं व समाज के प्रति उदासीन हो जाते हैं।
– ऑटिज्म से पीडि़त बच्चे उनके नाम बुलाने पर प्रतिक्रिया नहीं देते और अक्सर लोगों के साथ आंखों का संपर्क बनाने में बचते हैं।
– उन्हें यह जानने में मुश्किल होती है कि दूसरे क्या सोचते हैं और महसूस करते हैं। क्योंकि वे सामाजिक संकेत, बात करने के तरीके या चेहरे के भावों को नहीं समझ पाते और उचित व्यवहार करने के लिए जरूरी, लोगों के चेहरे को नहीं देखते।
– उन्हें सहानुभूति नहीं होती।
– ऑटिज्म से पीडि़त बच्चों को यह नहीं पता होता कि दूसरे बच्चों के साथ कैसे खेला जाए।
– कुछ मरीज गाना गाने की कम आवाज में अपनी बात उनसे कहते हैं जो उनके साथ उनके पसंदीदा विषय के बारे में और रूचि के साथ बात कर रहा हो। ऐसा लगता है जैसे वो अपनी ही एक दुनिया में हो, एक बुलबुले में।
2. मौखिक और अमौखिक संचार में होने वाली समस्याएं
– वे अन्य बच्चों की अपेक्षा बाद में बोलना शुरू करते हैं और मैं या मेरे की बजाय अपना नाम लेकर बातचीत करते हैं। बिगड़ा संचार, ऑटिज्म होने का सबसे जाना–पहचाना कारण है।
3. दोहराव या संकीर्ण व्यवहार, जूनूनी रूचियां
कई बच्चों में बार–बार हिलने या बालों को घुमाने जैसे दोहराव वाले व्यवहार शामिल होते हैं या फिर खुद को नुकसान पहुंचाने वाला व्यवहार जैसे काटने या सिर मारने जैसा व्यवहार करते हैं। ऑटिज्म वाले बच्चों में दर्द सहने की संवेदनशीलता कम हो जाती है लेकिन ध्वनि, छूने, असामान्य उत्तेजना के लिए असामान्य संवेदनशील रहते हैं। गले लगाने पर विरोध करना, ये असामान्य प्रतिक्रियाएं व्यवहार संबंधित लक्षणों को पहचानने में योगदान दे सकती हैं।
आम गलतफहमी
– ऑटिज्म से पीडि़त बच्चे अपनी भावनाओं को व्यक्त और महसूस नहीं कर सकते कि वे खुश हैं या दुखी
– कई लोग मौखिक रूप से अपनी बात कहने में अक्षम होते हैं जिसे मान लिया जाता है कि वे दोस्त नहीं बनाना चाहते।
– ऑटिज्म से पीडि़त बच्चे बौद्धिक रूप से अक्षम होते हैं। (जबकि तथ्य यह हैं कि ध्यान केंद्रित करने की योग्यता के कारण कई बच्चों का आई.क्यू सामान्य बच्चों से अधिक होता है।)
– बेकार देखभाल के कारण ऑटिज्म होता है।
थैरेपी
– ऑटिज्म के इलाज के लिए कोई विशेष दवा नहीं है लेकिन ऑटिज्म इंटरवेंशन प्लान से बच्चे के व्यवहार और संवेदी उपचार कर सुधार लाया जा सकता है।
– प्रत्येक ऑटिज्म वाले बच्चे या बड़े अलग होते हैं, इसीलिए प्रत्येक ऑटिज्म इंटरवेंशन प्लान को विशिष्ट योजनाओं के अनुरूप बनाया जाना चाहिए।
– शुरूआती गहन व्यवहार और संवेदी हस्तक्षेप में पूरा परिवार शामिल होता है जो पेशवरों की टीम के साथ मिलकर काम करता है। कई ऑटिज्म वाले लोगों अलग मेडिकल परिस्थितियां भी होती हैं जैसे स्लीप डिस्टर्बेंस, सीजरस और गेस्ट्रोइनटेस्टीनल डिजीज।
ऑटिज्म वाले बच्चों के साथ काम करने के टिप्स
– सुनिश्चित करें कि बोलकर और दिखाकर दिशा–निर्देशों को चरणबद्ध तरीके से दिये जाएं और उन्हें जरूरत पडऩे पर शारीरिक सहयोग भी दें।
– ऑटिज्म वाले लोगों को अक्सर चेहरे के भाव, बॉडी लैंग्वेज, आवाज को पहचानने में मुश्किल होती है। अपने निर्देशों को उसके सामने स्पष्ट करें।
– पता लगाएं कि मरीज की क्या खूबी हैं और उन पर जोर दें। उन्हें उस रास्ते ले जाएं और सफलता के अवसर बनाएं।
– सकारात्मक प्रतिक्रिया दें, काफी सारे अवसर देते हुए अभ्यास कराएं।
– उनकी नियमित दिनचर्या बनाए रखें। यदि आपको बच्चे दिनचर्या के परिवर्तन के बारे में पता है तो उसे पहले इस इस बारे में बताएं जिससे वह इस परिवर्तन के लिए पहले से तैयार हो जाए।